Surface Mount Technology – SMD PCB
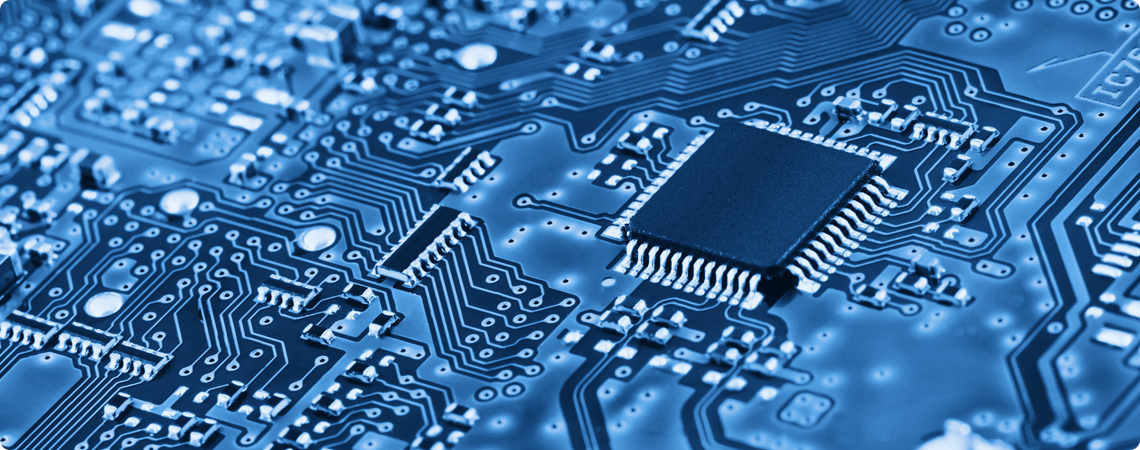
Surface-mount technology (SMT) is a component assembly technology related to PCB (printed circuit board) wherein the components are attached and connected on the surface of the board using batch solder-reflow processes.
SMT differs from other methods where the component leads are inserted into plated through-holes and wave-soldered from the bottom to fill in the holes and interconnect the components. Surface-mount technology has the advantages of achieving higher packaging densities, higher reliability, and reduced cost than the plated through-hole insertion process.
SMT allows automated PCB assembly and soldering to be used. This process is currently most widely used for low-cost, high-production consumer electronic assemblies.
What is SMD? – SMT devices
A surface-mount device (SMD) is an electronic device for which the components are mounted directly onto the surface of the printed circuit board (PCB).
Surface mount components are different to their leaded counterparts. Rather than being designed to wire between two points, SMT components are designed to be set down on a board and soldered to it. This method is the predominant method of technology used in electronic manufacturing.
The surface mount pads themselves must be flat to allow the solder paste screen stencil to engage perfectly with the surface of the PC board underprint.
Any lumps on the surface mount pads will cause a gap, and solder paste will bleed out from under the stencil placing solder paste. Such poor solder paste printing causes short circuits and solder balls and is a major cause of assembly failure. So PCB assemblers seek perfectly flat surface mount pads on bare PCBs.